Is Till Only Used to Describe Glacial Rock Movement
Glacial drift denotes any sedimentary material deposited from melting ice or meltwater streams. More evidence comes from glacial striations scratches on the bedrock made by blocks of rock embedded in the ice as the glacier moves.
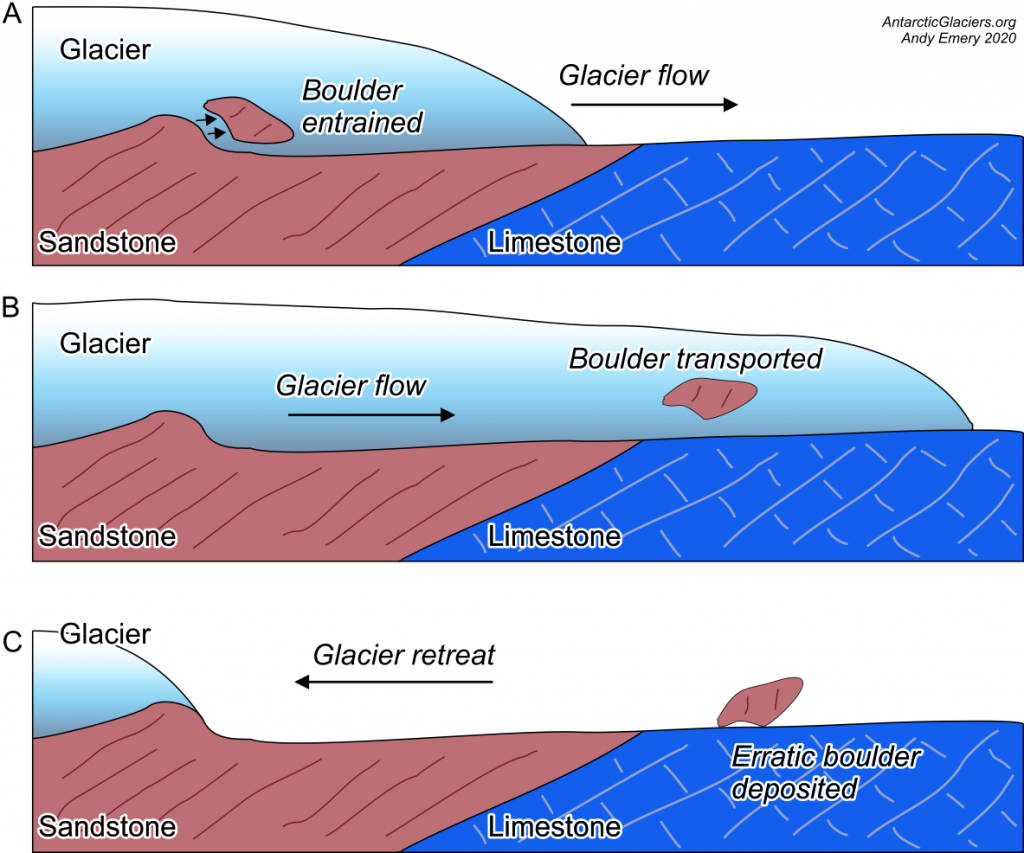
Glacial Erratics Antarcticglaciers Org
The principles of soil.
. These unsorted deposits of rock are called glacial till. Glacial till is a term used to describe parent materials that _____. Describe two components of glacial movement.
What word is used to describe glacial movement. Till - glacial ice melts drops its load of rock fragments. These unsorted deposits of rock are called glacial till.
Glacial striations rock flour causes meltwater streams to have cloudy appearance rock can be polished. What direction do glaciers flow. Glacial deposition is when sediment and rocks drop from land formations due to glacier movements.
Meltwater at the bottom of the glacier helps it to glide over the landscape. Are sorted by rapidly flowing melt waters. Prior to 1990 few field studies were pub-lished on this topic but research regarding fractured tills has evolved rapidly since then.
Landscape feature deposited by the ice glacial till C. Melting glaciers deposit all the big and small bits of rocky material they are carrying in a pile. 1 rock fragments or clasts 1 mm and 2 matrix till matrix are crushed and abraded to their terminal grain size mode.
Landscape feature carved by the glacial ice. Scratching nearby rocks when moved. An unsorted and unstratified accumulation of glacial sediment deposited directly by glacier ice.
A glacier will always flow in the direction the ice is sloping. Till is deposited directly by the glacier and stratified drift is rock debris laid down by glacial meltwater. The edges and upper layer of the glacier is not under as much pressure.
Indicates direction of glacial movement. Explain how basal sliding and internal flow facilitate the movement of ice from the upper part to the lower part of a glacier. These rocks can be carried for many kilometers for many years.
How does glacial till differ from stratified drift. A glacier might look like a solid block of ice but it is actually moving very slowly. Describe one glacial feature made of each type of glacial drift.
At the bottom of the glacier ice can slide over bedrock or shear subglacial sediments. Name three glacial features formed. In summary when the volumetric proportion of gravel is limited to 30 the gradation and size of the gravel only have a marginal influence on the mechanical characterization of the glacial till.
These show the direction of the glacier and suggest the ice flowed from a single central point. However a few selected reference citations are. The location of glaciers around the world.
These rocks that are different in type or origin from the surrounding bedrock are glacial erratics. As the ice in a valley glacier moves from the area of accumulation to that of ablation it acts like a conveyor belt transporting debris located beneath within and above the glacier toward its terminus or in the. Were transported by high winds during glacial periods D.
Learn more on this glacial till and. Debris in the glacial environment may be deposited directly by the ice till or after reworking by meltwater streams outwash. Were transported by water gushing from glacial fronts C.
What is a cirque. Glacial till is a term used to describe parent materials that contain a heterogeneous mixture of mineral debris dropped by receding glaciers The rate of chemical weathering is affected by the downward movement of water oxygen and inorganic acids flowing through the. The term is generally used to describe irregular mounds of sand gravel and till that accumulated in depressions or cavities in or on a stagnating glacier and dumped chaotically when the glacier melts May contain ice walled lakes kettles or kettle lakes.
There are very few known thin sections of flow tills see Meer 1985 Fig. Match the description letter with the following glacial features. Circular depression due to glacial erosion.
Landscape feature deposited by the melt-water outwash Lette r Feature Letter Feature Cirque U-Shaped Valley Drumlin Horn Esker Erratic Boulder Arête Hanging Valley. Typically where glacial diamictons tills are saturated and become deposited on slopes steeper than their bulk internal angle of friction whether in supraglacial or subglacial environments flow takes place and the resultant till is recognized as a flow till. The settling of sediments left behind by a.
The glacier moves because pressure from the weight of the overlying ice causes it to deform and flow. Acterization methods that have been used successfully in glacial till. Created by glacial retreat where sediment is.
The progressive growth and movement of a glacier. Were laid down in the bottom of former glacial lakes B. These rocks with a different rock type or origin from the surrounding bedrock are glacial erratics.
Evidence from the Permo-Carboniferous glaciation. Till is a heterogeneous mixture of different sized material deposited by moving ice lodgement till or by the melting in-place of stagnant ice ablation till. It is a landform made of till.
Plastic flow - movement within the ice. Melting glaciers deposit all the big and small bits of rocky material they are carrying in a pile. The breaking down of rocks by moving glaciers.
Like hot asphalt on a summer day. Stratified drift also called outwash denotes sand and gravel beds deposited from glacial meltwater streams. The resulting deposits are termed glacial drift.
Till is the end-product of glacial erosion transport comminution and deposition and consists of two particle size modes. Describe and identify the various landforms related to alpine glacial erosion including U-shaped valleys arêtes cols horns hanging valleys truncated spurs drumlins roches moutonées glacial grooves and striae. Till is the unsorted unstratified drift deposited directly as the ice melts.
Ice flow direction is determined by the glacier surface. Glaciers move by a combination of 1 deformation of the ice itself and 2 motion at the glacier base. Glacial tills have the most diverse range of particle size distribution of any soil yet within any category of glacial till it is possible to make some observations which help identify the type of till and how it will behave as shown in Figure 6 a ternary diagram highlighting the relationship between particle size distribution and description.
Many more references are available from the literature than can be provided in this review.
16 3 Glacial Erosion Physical Geology

Welcome To Coolgeography Co Uk Back To Main A Level Cold Environments Glacial Landforms Corries Aretes U Shaped Valleys Ribbon Lakes Hanging Valleys Glacial Deposition Roche Moutonnees Crag And Tail Drumlins How Corries Form Corries Form In

No comments for "Is Till Only Used to Describe Glacial Rock Movement"
Post a Comment